Networked Manufacturing
Networked Manufacturing is a flexible production model that is responsive to new materials and approaches and able to create a seamless circular flow of materials and design ideas
Bio-based, Local and Circular textile and garment production requires a different way of connecting producers, that is flexible and responsive to new materials and approaches and able to create a seamless circular flow of materials and design ideas. Conventional production models simply can’t accommodate different sustainable approaches and business models.
In this section you can find out about what it means to have a digitally networked approach to garment manufacturing, how this supports a circular economy model for textiles and what you can do to get started.
Why do we need new approaches to textile and garment manufacturing?
Textile manufacturing currently relies on global and linear supply chains. Clothing is often produced far away from where it is designed and where it will be used, meaning that it is difficult to ensure fair and sustainable practices are prioritised at every stage. Garments are shipped vast distances using fragile and energy-intensive transportation systems. New production models are greatly needed, such as networked manufacturing.
How can we enable networked manufacturing models?
Digitally connecting stakeholders through digital platforms can empower design teams and brands who want to transition to bio-based, local and circular manufacturing by making the necessary partnerships easier and more accessible.
Circular production approaches can also minimise textile and garment waste, through connection to local recyclers and re-use enterprises, and supporting appropriate circular decision-making at the design stage.
In HEREWEAR we explored a system of four different digital platforms to support circular, biobased and local networked manufacturing:
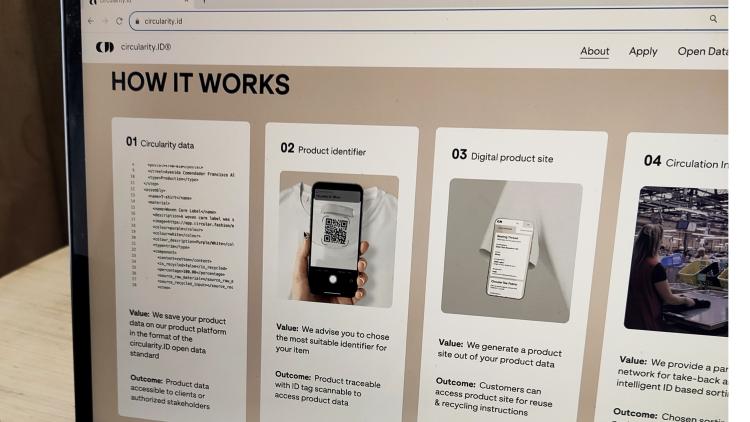
- A DIGITAL PRODUCT PASSPORT, such as circularity.ID allows stakeholders, including users, to access important product and service information, to make better choices about how to extend the life of the garment or recover the materials. https://circularity.id/
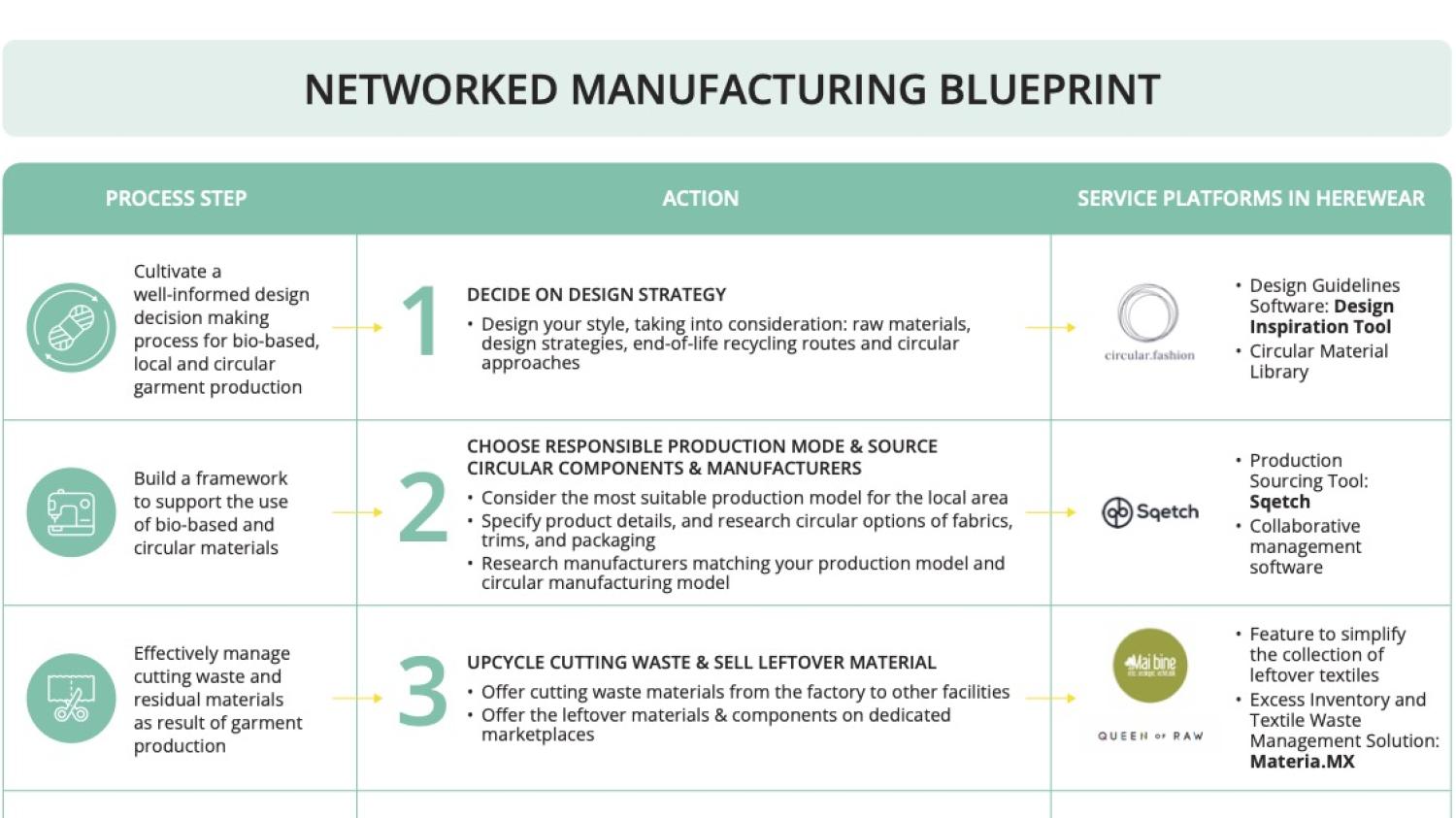
- A CIRCULAR DESIGN STRATEGY TOOL, such as the Decision Inspiration Tool, helps design teams choose a circular strategy for their garment design. https://circular.fashion/
- Then when the design is ready for production, design teams can locate and engage producers within PRODUCTION SOURCING PLATFORM, connecting brands with local producers without the burden of time-consuming research or difficult negotiations. This fosters effective relationships to produce more responsibly by having small batch runs, made-to-order and on-demand production. Within the platform designers and brands can create orders and complete all transactions. this was developed to 'proof of concept' in HEREWEAR but is not currently commercially available.
- A TEXTILE WASTE INVENTORY software extension, such as Materia.MX allows brands to resell their unused or leftover fabric. As all steps are digitised, the information is easily uploaded to a product passport for use by producers, customers, repairers and recyclers for greater transparency and improved circularity. https://www.queenofraw.com/
So, you want to develop a manufacturing network?
We have identified four steps in Bio-based, Local and Circular Textile Manufacturing:
- Decide for Circular Design Strategy
- Choose Your Responsible Production Mode and Source for Circular Components and Manufacturers
- Upcycle Your Cutting Waste and Re-sell Your Leftover Material
- Enrich Your Product Passport
Supporting the transition to Bio-based, Local and Circular Textile Manufacturing should also be based on a coherent system of actions on:
- Investment and Innovation
- Education and Awareness
- Regulation and Incentives
- Collaboration and Partnerships
- Consumer Engagement
- Supply Chain Optimisation